Homes Foreclosure Meaning
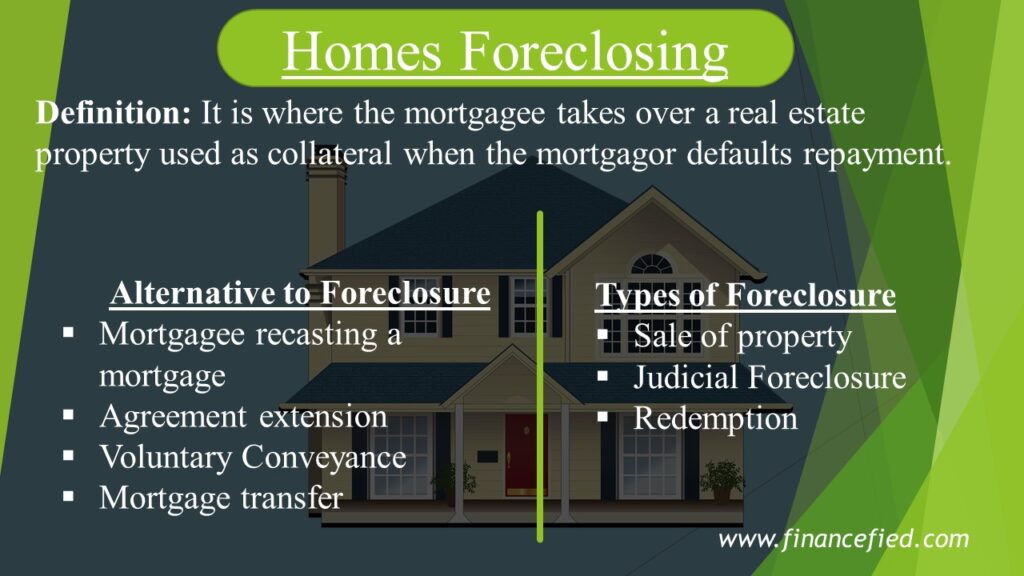
It is where the mortgagee takes over a real estate property used as collateral when the mortgagor defaults repayment. Foreclosure is expensive and lengthy; hence mortgagees often consider alternatives to foreclosure first.
Why Foreclosure is a Last Option?
- It is an expensive undertaking since costs must be incurred in court proceedings, auction costs, and even maintenance costs of the acquired property.
- Real estate property sold through auction is likely to sell at lower prices. Thus, the amount recovered is less than when an alternative option is used.
- In some cases, mortgagee might be unable to sell the acquired real estate property. It becomes a burden to manage and maintain such real estate assets.
Due to above reasons, the mortgagee is more likely to prefer an alternative option.
Read Also
Homeowners Insurance Definition, Types and Covers
Alternatives to Foreclosure
1. Mortgagee recasting a mortgage
The mortgagee can change the terms of a mortgage either temporarily or permanently to avoid any likelihood of mortgage default. Changes can be made on amounts payable, interest rates, amortization period, among others.
2. Agreement extension
Mortgagor and mortgagee can agree with each other to the extent the timeframe repay the mortgage. This can also be in the form of a temporary grace period to allow the mortgagor to accumulate money and repay. Before mortgagee extends mortgage repayment, the following must be ascertained:
- Intervening liens
- Real estate security must be in a good state
- Surety for any grantee who might have assumed the mortgage.
- If the mortgagee does now want to extend the repayment period formally, they can agree to an informal extension. Here, the mortgagor can waive the monthly payment for a mortgage.
3. Voluntary Conveyance
In a case where a mortgagor is not sure about their future ability to repay a mortgage, they can make arrangements to sell their assets to the mortgagee. If the asset is of higher value than the remaining mortgage balance, the mortgagee can agree to pay some sum back to the mortgagor.
This is a simpler way to settle the mortgage without foreclosure consideration. If the asset value is lower than the remaining mortgage amount, the mortgagee can accept such assets. This is because of the cost-benefit if the mortgagee would have considered a foreclosure.
4. Mortgage transfer
If one cannot meet their mortgage obligation and does not have any other alternative to pay back, a mortgagor can seek a person who can pay. Such a person will but the real estate property in question and assume all the mortgage obligations subject to the existing mortgage. A potential new owner will pay for a property whose value is high than the remaining mortgage.
Types of Foreclosure
1. Sale of property
Under this type of Foreclosure, the jurisdiction will be responsible for determining the entire process to sell the property. This includes but is not limited to the types of advertisement used for marketing such property and the method to use in such a sale.
2. Judicial Foreclosure
Two remedies apply for this type of Homes foreclosure:
i. The lender may sue the mortgagor on the unpaid amount, and after judgment, they can exercise what the court has decided against the mortgagor.
ii. The lender may bring a homes foreclosure suit to obtain a decree to exercise a foreclosure and sell the property in question.
3. Redemption
This is where the mortgagor pays off any amount related to their mortgage default. This could full payment of a mortgage or any interest accrued.
Summary
Related Articles:
- 4 Homeowners Insurance Coverages
- Important Functions and Benefits of Insurance
- Life Assurance and Life Insurance Definition
- Auto Insurance Definition and What it Covers
- Health Insurance Definition, Whats Covered and Whats Not
- Marine Insurance Definition, Importance and Marine Losses
- 6 Requisites of Insurability and Insurance Mechanism
